Movie Recommender from Spark 3.0.0 to Elasticsearch
Spark 3.0.0 release adds a new Factorization Machines regression model to its mllib and this is a great opportunity (for me) to revisit my first blog on factorization machines and this time train the model using spark.
In this post I will prepare the movielens dataset as input to sparks new FM model, train the FMRegressor and feed the documents to elasticsearch using the elasticsearch-spark library.
If you are not familiar with factorization machines or elasticsearch you should start here.
The full code in my github.
Prepare Data
The input to a Factorization Machines model is a list of events where each row represents a user rating a movie together with all the other features - age, gender and occupation. For example
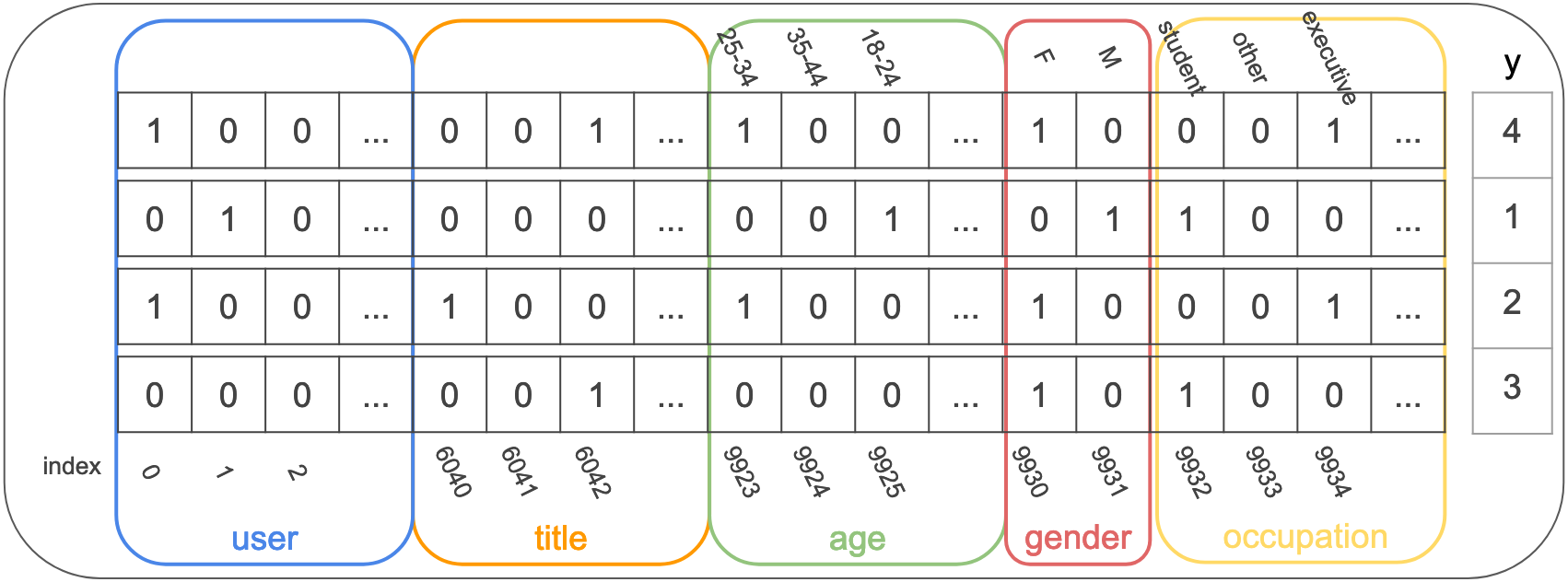 figure 1
figure 1
Sparks mllib FMRegressor expects this list to be represented by a dataframe with a rating (label) column and a features column that is a sparse vector like this:
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
|features |rating|
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
|(9953,[0,6042,9923,9930,9934],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|4 |
|(9953,[1,7858,9925,9931,9932],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|1 |
|(9953,[0,6040,9923,9930,9934],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|2 |
|(9953,[9,6042,9929,9930,9932],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|3 |
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
The sparse vector format is (<vector_size>,<indices>,<values>). All the vectors in this case have the same size 9953 which is the number of feature values and all the values in this case are 1. The first row is the event that user 0 rated movie 6042 (‘Til There Was You (1997)) with 4, the other features are
- age 9923: 25-34
- gender 9930: Female
- occupation 9934: “executive/managerial”
The following stages show how to transform the movielens dataset into this input dataframe.
Read movies file and create a unique index for each title using StringIndexer
val movies = spark.read.option("delimiter","::")
.csv(ml1mPath+"/movies.dat")
.toDF("movie_id","title","genres")
val titleIndexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("title")
.setOutputCol("title_index")
.fit(movies)
val moviesIndexed = titleIndexer.transform(movies)
Read users file and create a unique index for each user feature: user_id, gender, age, occupation. Each feature is in a different column so I use a pipeline of indexers
val users = spark.read.option("delimiter","::")
.csv("ml-1m/users.dat")
.toDF("user_id","gender","age","occupation","zipcode")
val userFeaturesIndexers = Array("user_id","gender","age","occupation")
.map(col => new StringIndexer().setInputCol(col).setOutputCol(col+"_index"))
val pipe = new Pipeline().setStages(userFeaturesIndexers).fit(users)
val usersIndexed = pipe.transform(users)
Join everything with ratings data
val ratings = spark.read.option("delimiter","::")
.csv("ml-1m/ratings.dat")
.toDF("user_id","movie_id","rating","time")
.withColumn("rating",$"rating".cast(IntegerType))
val ratingsJoined = ratings
.join(usersIndexed,Seq("user_id"))
.join(moviesIndexed,Seq("movie_id"))
ratingsJoined.select((featureColumns:+"rating").map(col):_*).show(4)
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
|user_id_index|title_index|age_index|gender_index|occupation_index|rating|
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
| 0.0| 2571.0| 6.0| 1.0| 11.0| 5|
| 0.0| 1818.0| 6.0| 1.0| 11.0| 3|
| 0.0| 2399.0| 6.0| 1.0| 11.0| 3|
| 0.0| 1096.0| 6.0| 1.0| 11.0| 4|
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
This is the list of events but each column contains indices ranging from 0 to size of feature - gender_index has values [0,1], title_index has values [0-3096] (3096 unique titles) etc. I need to shift the columns values so that each feature starts from the correct offset just like in figure 1. To add the offset, first calculate the size of each feature and then calculate the cumulative sum up until each feature:
Calculate the size of each feature using countDistinct
// movies feature size
val numMovies = moviesIndexed
.select(countDistinct($"title_index").alias("numMovies"))
.take(1)(0).getAs[Long]("numMovies")
// users features sizes
val userfeatureColumns = Seq("user_id_index","age_index","gender_index","occupation_index")
val userFeaturSizesDf = usersIndexed
.select(userfeatureColumns.map(c => countDistinct(col(c)).alias(c)): _*)
val userFeatureSizes = Map(userfeatureColumns
.zip(userFeaturSizesDf.take(1)(0).toSeq.map(_.asInstanceOf[Long])):_*)
val featureSizes = userFeatureSizes + ("title_index"->numMovies)
println(featureSizes)
Map(user_id_index -> 6040, age_index -> 7, title_index -> 3883, occupation_index -> 21, gender_index -> 2)
Calculate cumulative sum until each feature using scanLeft
val featureOffsets = Map(featureColumns
.zip(featureColumns.scanLeft(0L)((agg,current)=>agg+featureSizes(current)).dropRight(1)):_*)
println(featureOffsets)
Map(user_id_index -> 0, age_index -> 9923, title_index -> 6040, occupation_index -> 9932, gender_index -> 9930)
Add the correct offset to each column
val ratingsInput = ratingsJoined
.select(featureColumns.map(name=>(col(name) + lit(featureOffsets(name))).alias(name)):+$"rating":_*)
ratingsInput.show(10)
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
|user_id_index|title_index|age_index|gender_index|occupation_index|rating|
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
| 0.0| 8611.0| 9929.0| 9931.0| 9943.0| 5|
| 0.0| 7858.0| 9929.0| 9931.0| 9943.0| 3|
| 0.0| 8439.0| 9929.0| 9931.0| 9943.0| 3|
| 0.0| 7136.0| 9929.0| 9931.0| 9943.0| 4|
+-------------+-----------+---------+------------+----------------+------+
Each column is now starting from the correct offset. Next convert each row to a sparse vector column using a udf
val createFeatureVectorUdf = udf((size:Int,
user_id_index:Int,
movie_index:Int,
age_index:Int,
gender_index:Int,
occupation_index:Int) =>
Vectors.sparse(size,Array(user_id_index,movie_index,age_index,gender_index,occupation_index),Array.fill(5)(1)))
val data = ratingsInput
.withColumn("features",createFeatureVectorUdf(lit(featureVectorSize)+:featureColumns.map(col):_*))
data.select("features","rating").show(10,false)
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
|features |rating|
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
|(9953,[0,8611,9929,9931,9943],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|5 |
|(9953,[0,7858,9929,9931,9943],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|3 |
|(9953,[0,8439,9929,9931,9943],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|3 |
|(9953,[0,7136,9929,9931,9943],[1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0])|4 |
+----------------------------------------------------+------+
Data is ready!
Train Model
split data to train and test
val Array(trainset, testset) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.9, 0.1))
Create FMRegressor with embedding size 120 and fit on trainset
val fm = new FMRegressor()
.setLabelCol("rating")
.setFeaturesCol("features")
.setFactorSize(120)
.setMaxIter(300)
.setRegParam(0.01)
.setStepSize(0.01)
val model = fm.fit(trainset)
Evaluate rmse on testset
val predictions = model.transform(testset)
val evaluator = new RegressionEvaluator()
.setLabelCol("rating")
.setPredictionCol("prediction")
.setMetricName("rmse")
val rmse = evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
print(s"test rmse = $rmse")
test rmse = 0.866
My pytorch model on the same data had 0.85 rmse so some more parameter tuning is needed here.
Save model in table format and not model.write.save() because elasticsearch code will be running on spark 2.4.
Note: elasticsearch-spark is not compatible with scala 2.12 (yet) so the code is divided to 2 projects and some backflips where needed to read saved models from spark 3.0.0
val matrixRows = model.factors.rowIter.toSeq.map(_.toArray).zip(model.linear.toArray)
.zipWithIndex.map { case ((a, b), i) => (i, b, a) }
spark.sparkContext
.parallelize(matrixRows)
.toDF("index","bias","embedding")
.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).option("header","true").parquet("model_raw")
Index Documents to Elasticserach
In elasticsearch each document will represent a single feature value and will contain its index, type (user, movie, age, gender, occupation), embedding and bias. Elasticsearch-spark library expects a dataframe where each row is a document, the next stages will create these document dataframes:
Read saved model
val model = spark.read.option("header","true").parquet(modelPath)
model.show(4)
+-----+-------------------+--------------------+
|index| bias| embedding|
+-----+-------------------+--------------------+
| 5805|0.13825787734251777|[-0.0555360040031...|
| 5806|0.08648875415747574|[-0.0458145621058...|
| 5807|0.11548980867642408|[-0.0769451271770...|
| 5808|0.15566420826441005|[-0.0621027883297...|
+-----+-------------------+--------------------+
Create movie documents by joining the model with moviesIndexed on index column
val movieDocs = moviesIndexed
.join(model,$"title_index"===$"index")
.withColumn("feature_type",lit("movie"))
.withColumn("id",concat(lit("movie_"),$"index"))
.select("id","feature_type","embedding","bias","title")
movieDocs.show(4)
+----------+------------+--------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
| id|feature_type| embedding| bias| title|
+----------+------------+--------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
|movie_6067| movie|[-0.0256981204269...|0.09892066531869206| 52 Pick-Up (1986)|
|movie_6433| movie|[0.00727216899600...|0.09036617030523138| Big Daddy (1999)|
|movie_6454| movie|[-0.0589911762405...|0.11337237570085894|Birdcage, The (1996)|
|movie_6653| movie|[-0.0533178530852...|0.11667342783518653| Captives (1994)|
+----------+------------+--------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
Feed documents to elasticsearch using saveToEs
movieDocs.saveToEs("recsys",Map("es.mapping.id" -> "id"))
Create user feature documents also by joining with model (remember indices are all unique) and feed to elasticsearch
val userfeatureColumns = Seq("user_id","age","gender","occupation")
// Each iteration takes care of a different feature
userfeatureColumns.foreach(columnName =>
usersIndexed
.dropDuplicates(columnName+"_index")
.join(model, col(columnName+"_index")===$"index")
.withColumn("feature_type",lit(columnName))
.withColumn("id",concat(lit(columnName+"_"),$"index"))
.select("id","feature_type","embedding","bias")
.saveToEs("recsys",Map("es.mapping.id" -> "id")))
Thats it elasticsearch index is ready for recommending movies! check out previous post for setting up elasticsearch and query stages.